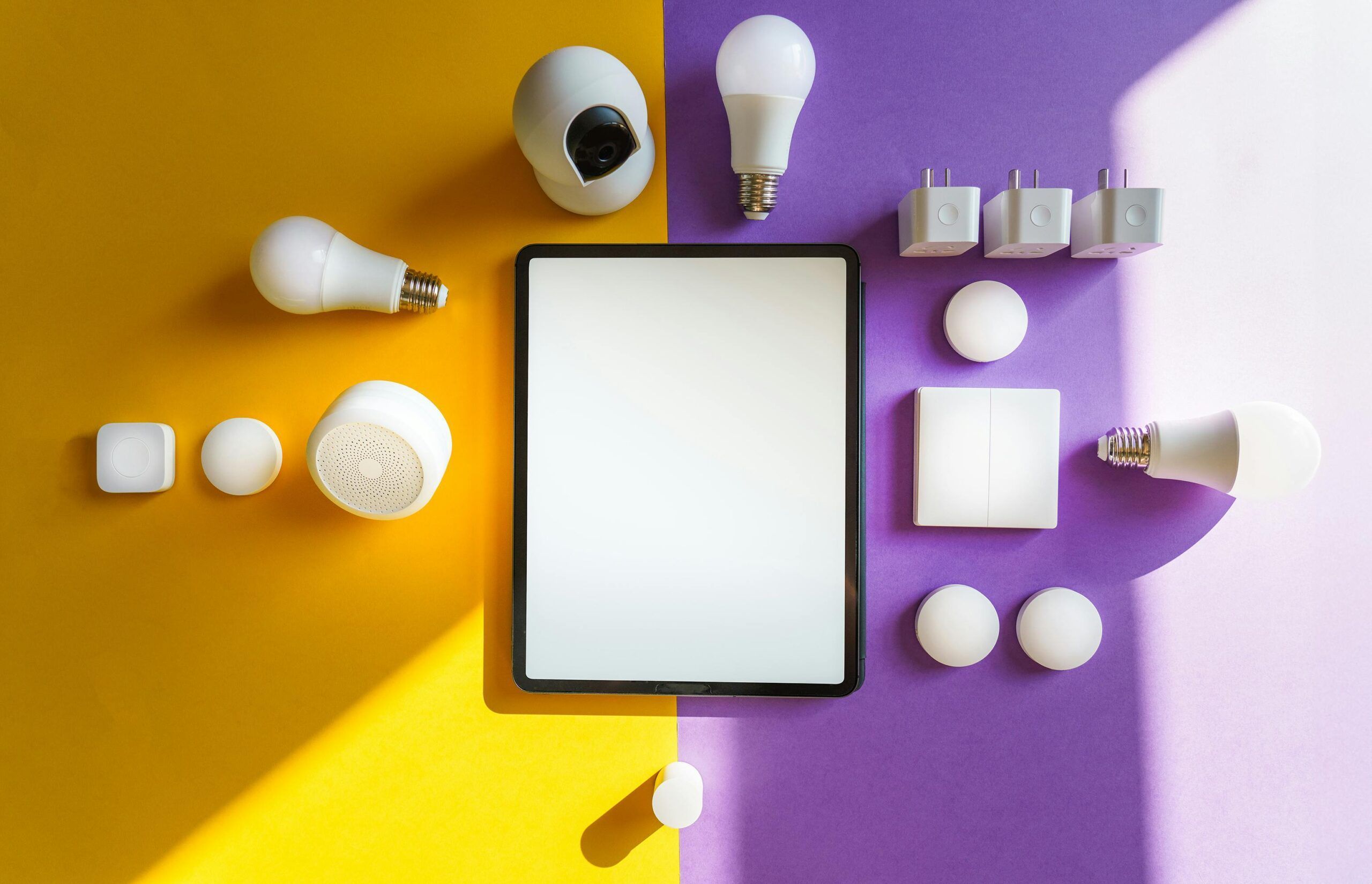
The Internet of Things (IoT) is one of the most powerful technological revolutions of the 21st century. From smart home gadgets to industrial automation, IoT is revolutionizing how we live, work, and interact with the world around us. As billions of devices get connected globally, IoT is forging a future where data and connectivity drive smarter decisions, efficiency, and creativity.
What Is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices that communicate and share data through the internet. These devices—ranging from smartphones, wearables, and smart appliances to industrial machines—collect data from their environment and respond intelligently to orders.
In simple terms, IoT turns everyday objects become “smart” devices .
For example:
Your smartwatch tracks your fitness and provides information to your phone.
A smart refrigerator notifies you when you’re running low on groceries.
Security cameras give live updates directly to your smartphone.
IoT enables automation and intelligent decision-making without human intervention, creating a linked world where everything from your automobile to your coffee machine can interact effortlessly.
How Does IoT Work?
IoT functions through a combination of sensors, connection, data processing, and user interfaces .
-
- Sensors and Devices — These collect real-time data such as temperature, location, or motion.
-
- Connectivity — The data is transferred by Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, 5G, or satellite networks.
-
- Cloud and Data Processing – The acquired data is processed in the cloud or at the network edge to make intelligent decisions.
-
- User Interface — The insights are provided through applications, dashboards, or voice assistants (like Alexa or Google Assistant). This seamless connectivity lets devices to do tasks automatically—for instance, your thermostat changing room temperature based on your behaviors or your car transmitting maintenance notifications before a breakdown.
Real-World Applications of IoT
The applications of IoT are vast and developing across various sectors.
🏠 Smart Homes Smart home technology is one of the most common uses of IoT. Devices like smart lighting, thermostats, and voice assistants make homes more pleasant, secure, and energy-efficient.
🏥 Healthcare and Wearables IoT-enabled healthcare devices monitor vital signs such as heart rate, oxygen levels, and sleep patterns, transmitting data straight to clinicians for remote diagnosis and treatment.
🚗 Smart Transportation Connected automobiles employ IoT to improve safety and navigation. Real-time traffic data helps optimize routes, while autonomous cars use sensors and AI for self-driving capabilities.
🏭 Industrial IoT (IIoT) In manufacturing, IoT sensors monitor equipment health, predict breakdowns, and increase production efficiency. This reduces downtime and promotes workplace safety.
🌆 Smart Cities IoT underpins smart city programs, like automatic traffic lights, garbage management, and energy-efficient lighting. These advances improve urban living and sustainability.
🌾 Agriculture IoT helps farmers monitor soil conditions, water levels, and crop health in real time. This leads to greater crop yields and optimized resource consumption.
Key Benefits of IoT
The Internet of Things offers various advantages that make it a game-changer for both individuals and businesses:
-
- Automation and Efficiency: Tasks are accomplished automatically, saving time and effort.
-
- Real-Time Monitoring: IoT gives fast access to crucial data, boosting decision-making.
-
- Cost Reduction: Predictive maintenance minimizes repair costs and prevents system breakdowns.
-
- Enhanced Safety and Security: Smart alarms and surveillance systems protect people and assets.
-
- Convenience: IoT simplifies daily life—turning gadgets on or off with a tap or voice command.
Challenges and Risks of IoT
Despite its immense promise, IoT faces numerous problems that must be addressed for long-term success:
Data Privacy: With so much data collected, privacy concerns are a serious issue.
Cybersecurity Threats: Unsecured devices might be exposed to hacking or data theft.
Device Compatibility: Different manufacturers employ distinct communication standards, making integration difficult. High Initial Costs: Setting up large-scale IoT networks can be expensive initially.High Initial Costs: Setting up large-scale IoT networks can be expensive initially
To solve these issues, firms must invest in strong security protocols, encryption, and regular updates to secure linked systems.
The Future of IoT
future of the Internet of Things is tremendously bright. Experts predict that by 2030, there will be over 30 billion linked devices worldwide. Emerging technologies like 5G , Artificial Intelligence (AI) , and Edge Computing are bringing IoT to the next level.
AIoT (Artificial Intelligence + IoT): AI enables IoT devices make smarter, real-time choices without human input.
5G Networks: Faster connectivity allows devices to share data instantly.
Edge Computing: Processes data near the source instead than relying only on cloud computing, enhancing speed and reliability.
In the future years, we can expect a completely connected environment where IoT enhances healthcare, transportation, commercial operations, and daily living on a global scale.
Conclusion:
The Internet of Things (IoT) is not merely a technology trend—it’s the foundation of a smarter, more efficient world. By connecting billions of objects and enabling real-time communication, IoT has already begun altering industries and everyday life.However, as we continue to utilize IoT on a greater scale, data security, privacy, and ethical use of technology must remain major objectives.
With the correct combination of innovation and regulation, IoT will continue to alter how we interact with technology—making our world truly intelligent, connected, and sustainable.